专栏文章
Solution of CF207B3 Military Trainings
CF207B3题解参与者 1已保存评论 0
文章操作
快速查看文章及其快照的属性,并进行相关操作。
- 当前评论
- 0 条
- 当前快照
- 1 份
- 快照标识符
- @mir1pm1q
- 此快照首次捕获于
- 2025/12/04 14:19 3 个月前
- 此快照最后确认于
- 2025/12/04 14:19 3 个月前
你可以浏览这个题解的中文版本。
The images are hosted on Github, use an accelerator if it fails to load.
It is first easy to think of duplicating the sequence over and over again, breaking the ring into a chain, with each query i.e. querying a sub-segment answer.
Let be transferable from or , and consider a greedy.
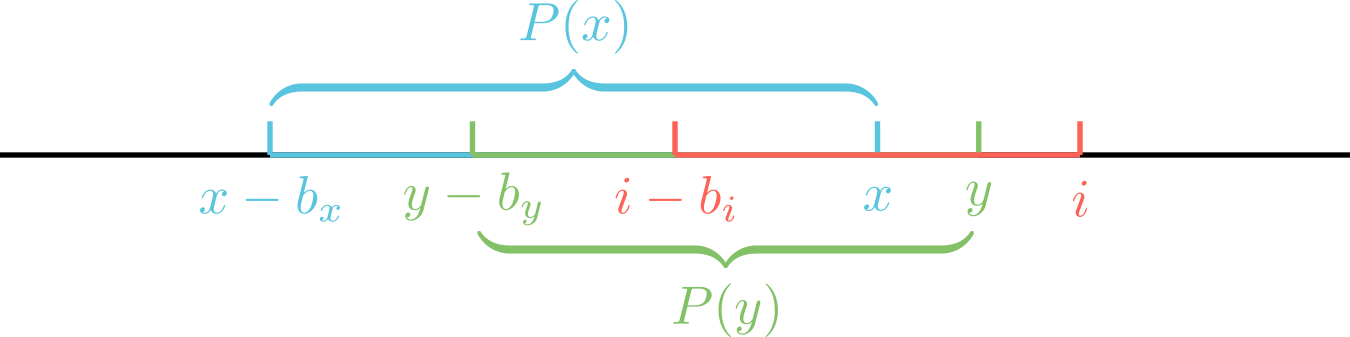
where denotes the points from which can be transferred, i.e. .
Since holds, we do not need to consider the contribution of the interval . Instead, , i.e., all points that can be transferred to can be transferred to , so it is sufficient to choose a transfer from . That is, it is not inferior to transfer from the smaller of . Maintained in ST tables, complexity .
You submited the code and found it accepted in the simulation game. You can use multiplicative preprocessing to figure out where you can jump steps, optimising to .
相关推荐
评论
共 0 条评论,欢迎与作者交流。
正在加载评论...