专栏文章
【题解】 比太郎之旅
题解参与者 4已保存评论 3
文章操作
快速查看文章及其快照的属性,并进行相关操作。
- 当前评论
- 2 条
- 当前快照
- 1 份
- 快照标识符
- @mindgi3b
- 此快照首次捕获于
- 2025/12/02 00:36 3 个月前
- 此快照最后确认于
- 2025/12/02 00:36 3 个月前
背景
出到了校内模拟赛中,写出目前没有的 的做法,获得了本题最优解。
题意
你有 个点,第 个点位于坐标 ,现在有一个人从 坐标出发,每次选择目前的离他最近且没有到达过的点,问他最后遍历完所有点时坐过的距离和,多次询问。
思路
我们先考虑从每个点出发的答案,记作 。
首先 ,含义是从第一个点出发肯定直接从左往右走就行了。
之后我们考虑 的情况,我们考虑从二号点出发的答案一定是先往右走一段,如果走到 了,走回来就行了,如果没有走到 ,那么就要先回到 号点,然后走到 号点,接下来我们只需要解决从每个点出发往右走一直能够走到哪里就行了。
我们考虑如何计算往右能走到哪? 把这个东西记作 。
对于相邻的两个点 之间的连边,我们计算 在什么时候会被当作最靠右的边,这种贡献的点就是一个从 往前的后缀,证明:我们写一下表达式,如果 能到达 并且在到达 时往回走,那么就有表达式: 我们移一下项,就有: 这个是好二分的,那么我们就可以通过写一个维护区间取 ,修改完后单点查询的数据结构,笔者这里写的是
multiset。现在我们已经解决了从 开始的答案,现在我们尝试往 推广,如图:
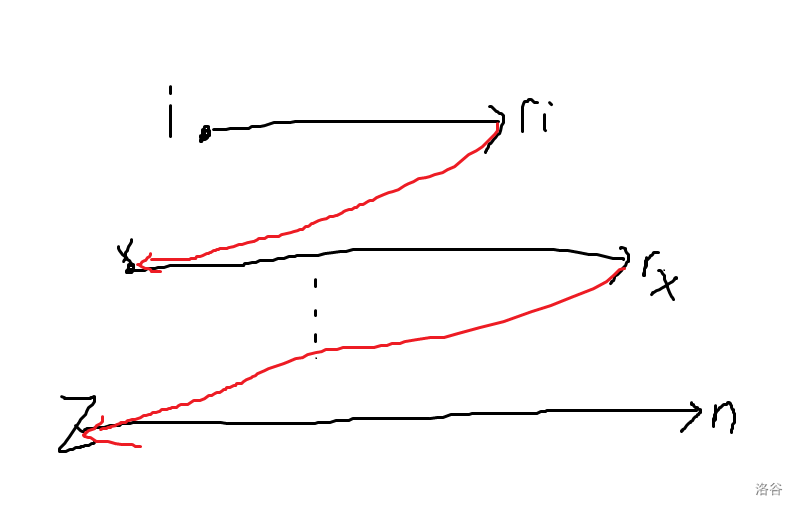
我们走的路线一定可以刻画成上面那种模式,考虑从 开始的答案一定是从 走到 ,在往回走到 ,之后就转化为从 开始的长度。
那么我们只需要能求出来 就能通过递推的方式转移出来答案。
假如说我们现在确定从 走到 ,那么我们如何求出 呢?
注意到 是满足以下条件中最大的那个:
第一个限制是好做的,现在我们考虑如何满足第二个限制。
我们变一下型,可以转化为:,我们发现右边对于相同的 而言是个定值,且 满足条件的 一定是一段从 开始的前缀,又可以二分了,我们记 表示 最大能去到哪里。
那么上述的第两个条件就转化为:
这个我们再变一下型:
由于我们要求的是最小的 ,所以我们只需要用个能够支持静态查询区间最大值的数据结构加上二分就可以了,笔者这里写的是 st表。
我们已经求出来 了,那就有转移:
最后他让求的是从任意坐标开始的答案,我们找到离我们询问最近的点就行了。
分析一波复杂度,求 是 的,求 是 的,一次询问是 返回,总复杂度为 。
代码
CPP#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define uint unsigned long long
#define double long double
#define Air
namespace io{inline int read(){int f=1,t=0;char ch=getchar();while(ch<'0'||ch>'9'){if(ch=='-')f=-f;ch=getchar();}while(ch>='0'&&ch<='9'){t=t*10+ch-'0';ch=getchar();}return t*f;}inline void write(int x){if(x<0){putchar('-');x=-x;}if(x>=10){write(x/10);}putchar(x%10+'0');}}
using namespace io;
int n, q;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int a[N];
int rid[N];
int tid[N];
int ans[N];
vector<int>stt[N], edd[N];
int st[21][N];
int pre[N];
int st_ask(int x, int y){
int step = pre[y - x + 1];
return max(st[step][x], st[step][y - (1ll << (step)) + 1]);
}
signed main() {
#ifndef Air
freopen("bitaro.in","r",stdin);
freopen("bitaro.out","w",stdout);
#endif
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);cin.tie(0);cout.tie(0);
n = read();
rid[1] = n;
pre[1] = 0;
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
pre[i] = pre[i / 2] + 1;
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
a[i] = read();
}
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
if(i >= 2){
rid[i] = lower_bound(a + 1, a + 1 + n, a[i] + a[i] - a[i - 1]) - a - 1;
}
st[0][i] = rid[i];
}
for(int i = 1; i <= 20; i ++){
for(int j = 1; j + (1ll << (i)) - 1 <= n; j++){
st[i][j] = max(st[i - 1][j], st[i - 1][j + (1ll << (i - 1))]);
}
}
for(int i = 2; i < n; i++){
int dis = a[i + 1] - a[i];
int tmp = lower_bound(a + 1, a + i, a[i] - dis) - a;
if(tmp == i) continue;
stt[tmp + 1].push_back(i);
edd[i + 1].push_back(i);
}
ans[1] = a[n] - a[1];
multiset<int>mt;
mt.insert(n);
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
for(auto y: stt[i]){
mt.insert(y);
}
for(auto y: edd[i]){
mt.erase(mt.find(y));
}
tid[i] = *mt.begin();
}
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++){
if(tid[i] == n) {
ans[i] = a[n] - a[i] + a[n] - a[1];
continue;
}
int l = 1, r = i - 1;
while(l + 1 < r){
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if(st_ask(mid, i - 1) > tid[i]){
l = mid;
}
else{
r = mid;
}
}
int pos = 0;
for(int j = r; j >= l; j--){
if(st_ask(j, i - 1) > tid[i]){
pos = j;
break;
}
}
ans[i] = ans[pos] + a[tid[i]] - a[i] + a[tid[i]] - a[pos];
}
q = read();
while(q--){
int x = read();
if(x >= a[n]){
cout << ans[n] + (x - a[n])<< '\n';
continue;
}
if(x <= a[1]){
cout << ans[1] + (a[1] - x) << '\n';
continue;
}
int tmp = lower_bound(a + 1, a + 1 + n, x) - a;
if(a[tmp] - x < x - a[tmp - 1]){
cout << ans[tmp] + a[tmp] - x << '\n';
}
else{
cout << ans[tmp - 1] + (x - a[tmp - 1]) << '\n';
}
}
return 0;
}
相关推荐
评论
共 3 条评论,欢迎与作者交流。
正在加载评论...